An example of malspam pushing Lokibot malware, November 2019
Introduction
I posted two diaries last year (2018) about Lokibot malware (sometimes spelled "Loki-bot"). One was in June 2018 and one was in December 2018. It's been a while, so I wanted to share a recent example that came to my blog's admin email on Tuesday 2019-11-12.
The email
You can get a copy of the sanitized email from this Any.Run link.
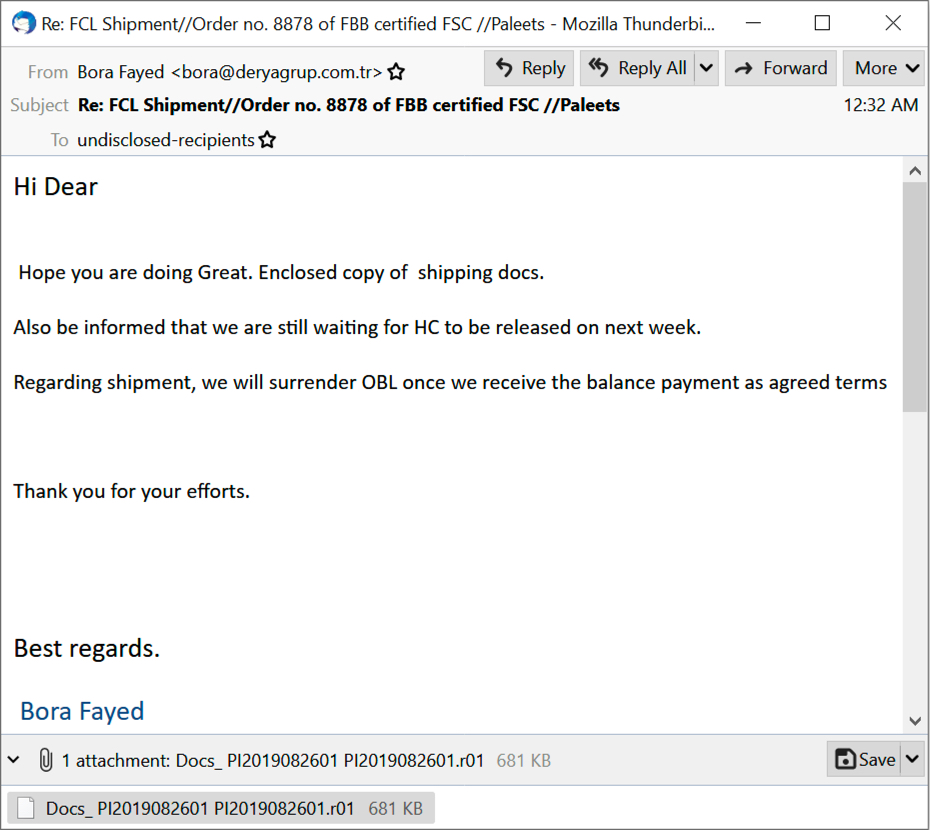
Shown above: A copy of the email opened in Thunderbird.
The attachment was a RAR archive (link) and the RAR archive contained a Windows executable file disguised as a PDF document (link).
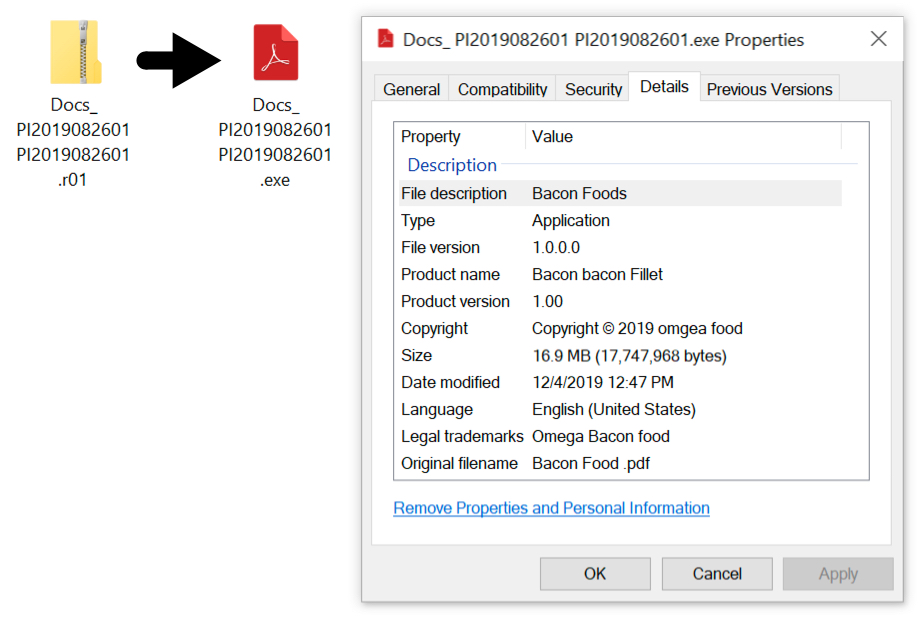
Shown above: The attached RAR archive and the extracted Windows executable file.
The infection traffic
Infection traffic is easily detectable by signatures from the EmergingThreats Open ruleset.
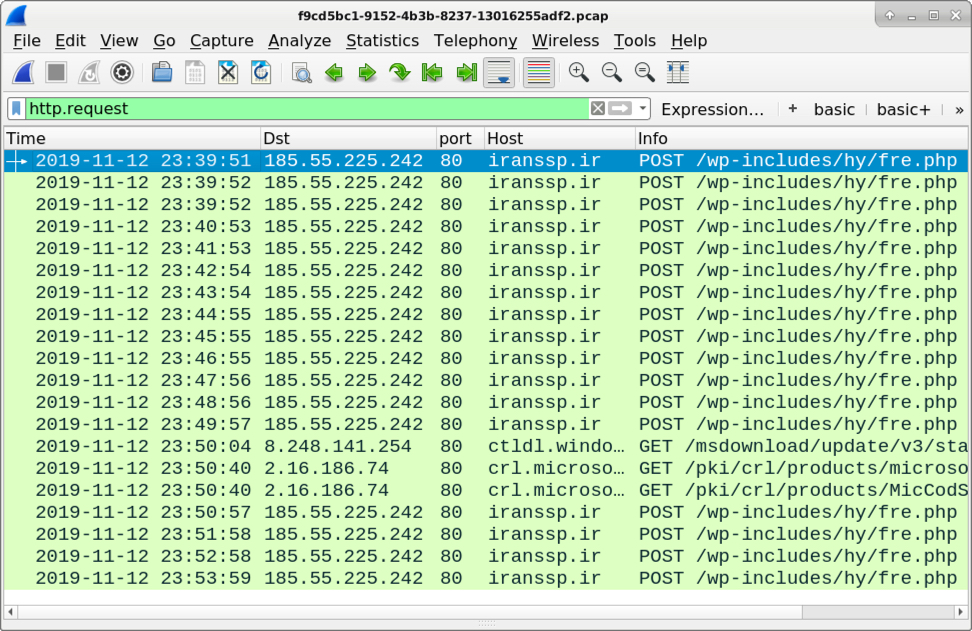
Shown above: Traffic from an infection filtered in Wireshark.

Shown above: TCP stream from one of the HTTP requests caused by my sample of Lokibot malware.
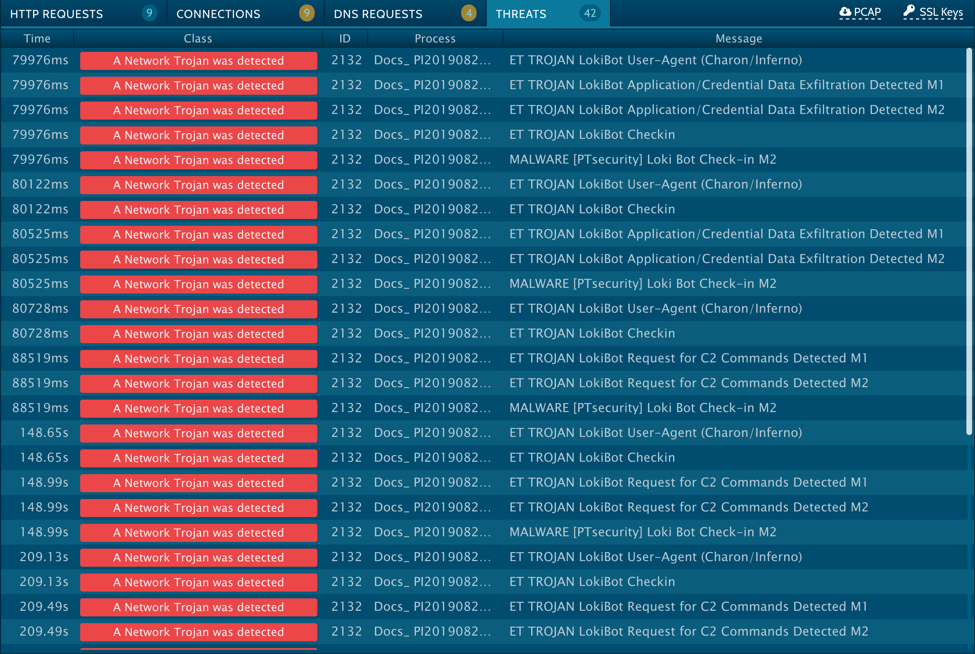
Shown above: EmergingThreats alerts from an Any.Run sandbox analysis of the Windows executable file.
Post-infection forensics on an infected Windows host
I was able to infect a Windows 10 host in my lab environment, and Lokibot made itself persistent through the Windows registry.
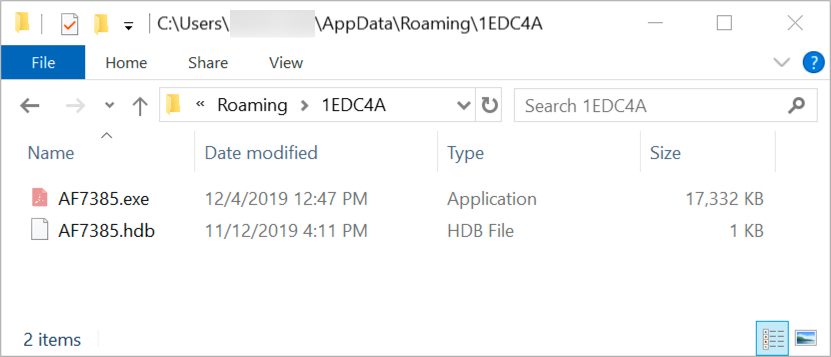
Shown above: Lokibot on an infected Windows host.
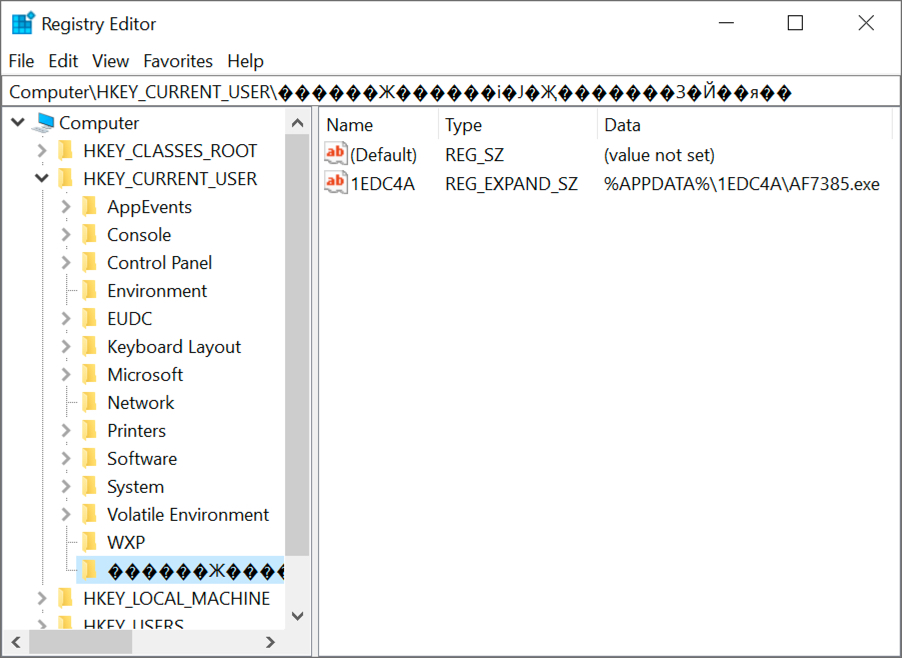
Shown above: Windows registry update caused by Lokibot to stay persistent.
Final words
SHA256 hash of the email:
SHA256 hash of the attached RAR archive:
SHA256 hash of the extracted Windows executable file (Lokibot malware):
--
Brad Duncan
brad [at] malware-traffic-analysis.net


Comments